Electronegativity is the capability of the nucleus in an atom to attract and retain all the electrons within the atom itself and depends on the number of electrons and the distance of the electrons in the outer shells from the nucleus.
Ceramics are formed by what bonds.
Most ceramics are made up of two or more elements.
These chemical bonds are of two types.
The atoms in ceramic materials are held together by a chemical bond.
Perhaps the most confusing decision for clinicians is bonding versus cementing of ceramic restorations.
An oxide oxide non oxide non oxide or oxide non oxide combinations.
The two most common chemical bonds for ceramic materials are covalent and ionic.
Ceramic restorations are an esthetic biocompatible and costeffective alternative to ceramic metal restorations.
They are either ionic in character involving a transfer of bonding electrons from electropositive atoms to electronegative atoms or they are covalent in character involving orbital sharing of electrons between the constituent atoms or ions.
Two types of bonds are found in ceramics.
This is called a compound.
According to this definition elemental carbon is a ceramic.
Underlying many of the properties found in ceramics are the strong primary bonds that hold the atoms together and form the ceramic material.
Many ceramics contain a mixture of ionic and covalent bonds between atoms.
1 2 zirconia based and lithium disilicate ceramics are rapidly growing segments within the ceramic category.
Graphene is currently considered the strongest known material.
Recall that the predominant bonding for ceramic materials is ionic bonding.
For example alumina al 2 o 3 is a compound made up of aluminum atoms and oxygen atoms.
Ceramic based composites are formed by.
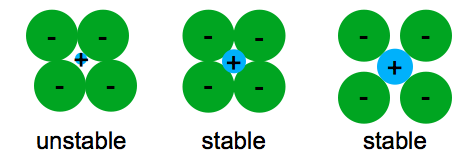
The ionic bond occurs between a metal and a nonmetal in other words two elements with very different electronegativity.
In ionic bonding a metal atom donates electrons and a nonmetal atom accepts electrons.
Additionally carbon based materials such as carbon fiber carbon nanotubes and graphene can be considered ceramics.
Ceramics may be glazed prior to firing to produce a coating that reduces porosity and has a smooth often colored surface.
The high energy of covalent bonds makes these ceramics very stable with regard to chemical and thermal changes.
A ceramic is an inorganic nonmetallic solid generally based on an oxide nitride boride or carbide that is fired at a high temperature.
Occur when two molecules combine releasing a smaller molecule usually water as the bond forms.
This electron transfer creates positive metal ions cations and negative nonmetal ions anions which are attracted to each other through coulombic attraction.
Most often fired ceramics are either vitrified or semi vitrified as is the case with earthenware stoneware and porcelain.
Covalent bonding is found in many ceramic structures such as sic bn and diamond.